Winter brings a range of challenges for cable systems, especially during periods of frost and snow. Cold temperatures, moisture, and ice can negatively impact the performance and durability of cables.
Proper warming measures must be implemented to ensure uninterrupted operation and safety.
This article ZMS Cable explores effective strategies for protecting cables from harsh winter conditions.
Cables exposed to extreme cold and snow are vulnerable to the following issues:
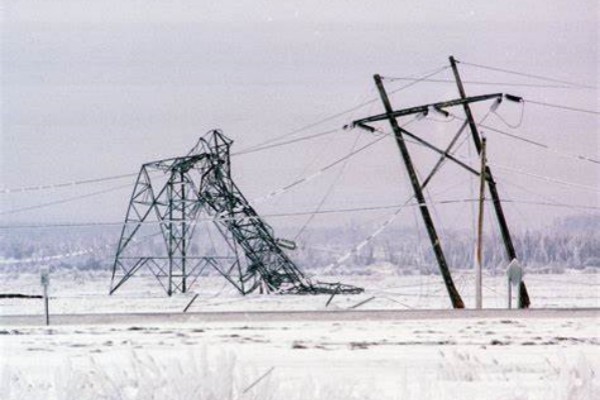

Brittleness of Insulation: Low temperatures can cause cable insulation, particularly PVC, to become brittle, increasing the risk of cracks or breaks.
Reduced Flexibility: Cold environments make cables less flexible, which can lead to mechanical stress and damage during installation or use.
Moisture Intrusion: Frost and snow can cause moisture to seep into cable connections, leading to short circuits or corrosion.
Increased Electrical Resistance: Low temperatures may alter the electrical properties of certain cable materials, impacting performance.
To mitigate the effects of frost and snow, the following warming measures can be applied:
Heat tracing systems involve installing electric heating elements along cables to maintain a stable temperature and prevent freezing.
Self-Regulating Heat Trace Cables: These adjust their heat output based on ambient temperature, ensuring energy efficiency.
Constant Wattage Heat Trace Cables: Provide a consistent heat output, ideal for applications requiring uniform warmth.
Heat tracing systems are especially useful for outdoor cables and those in regions with heavy snow.
Adding thermal insulation around cables is an effective way to maintain their temperature and reduce heat loss.
Foam-Based Insulation: Lightweight and durable, foam materials provide excellent thermal resistance.
Polyurethane or Rubber Jackets: These materials offer both insulation and protection against physical damage.
Ensure insulation materials are water-resistant to prevent ice formation.
Protective conduits shield cables from direct exposure to snow and frost.
Metal or PVC Conduits: Act as a barrier against external weather conditions.
Above-Ground Troughs or Enclosures: Prevent snow accumulation and ensure proper drainage.
For underground installations, ensure the conduits are buried below the frost line.
Proactive maintenance can identify potential issues before they escalate:
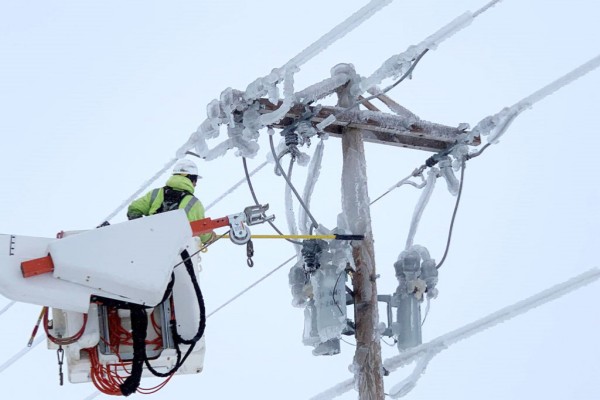

Pre-Winter Inspections: Check for cracks in insulation, loose connections, and corrosion.
Thermal Scanning: Use infrared cameras to detect temperature irregularities in cable systems.
Cleaning and Sealing: Remove dirt and moisture from connectors and apply waterproof seals.
Preventing ice formation on and around cables is crucial:
De-Icing Sprays: Apply chemical sprays designed for cable applications to prevent ice buildup.
Heated Mats or Wraps: Wrap cables with electric mats to keep them above freezing temperatures.
For areas prone to extreme cold, select cables specifically designed for winter conditions:
Low-Temperature PVC or XLPE Cables: These materials remain flexible and durable in subzero temperatures.
Silicone Insulated Cables: Highly cold-resistant, these are ideal for industrial applications.

Different environments require unique approaches to cable protection during winter:
Implement heat tracing systems for power and control cables running outdoors.
Insulate cable trays and junction boxes to avoid moisture accumulation.
Use protective conduits for outdoor power lines supplying electricity to homes.
Install GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) systems to detect and mitigate moisture-related faults.
Railways: Equip high-voltage railway cables with anti-icing systems to prevent disruptions.
Airports: Use heated conduits for runway lighting and signaling cables.
Proper cable warming measures offer multiple advantages:
Enhanced Durability: Protect cables from physical and environmental damage.
Improved Safety: Minimize risks of electrical fires and short circuits.
Uninterrupted Operations: Ensure consistent performance in critical systems.
Cost Savings: Reduce maintenance and replacement costs by extending cable life.
Documentation: Keep a record of cable types, locations, and warming measures applied for future reference.
Training: Educate maintenance personnel on winter cable protection techniques.
Emergency Kits: Stock de-icing sprays, thermal blankets, and repair tools for quick response to winter emergencies.
Advances in cable technology are making it easier to manage winter challenges:
Smart Heat Tracing Systems: Automated systems with IoT integration for real-time temperature monitoring.
Nano-Coated Insulation Materials: Offer enhanced thermal resistance and waterproofing.

Self-Healing Insulation: Repairs minor cracks or damages caused by cold weather automatically.
Winter conditions can pose significant risks to cable systems, but these challenges can be effectively managed with the right warming measures.
From heat tracing systems and thermal insulation to the use of winter-grade cables, implementing these strategies ensures optimal performance and longevity.
By proactively protecting cables against frost and snow, businesses and homeowners can enjoy safe, uninterrupted operations even in the harshest winter climates.